GPT's: How is the narrative shifting?
(Maps viewable on desktop only)
We took over 120,000 social media and news posts mentioning AI over the past 18 months, in order to measure how the conversation is evolving. How are people experiencing this technology, and what do they have to say? After filtering specifically for GPT-related posts, the total netted out to 32k
The axes and clusters are based on the language in the posts and are unique to this dataset, from trillions of possible combinations. This customized clustering helps to avoid the bias and blindspots of pre-set categories.
Every dot in the map below represents a single post. Hover over the dots with your cursor. Note the slider on the lower right of the map below. The 4-cluster view shows the high-level axes of the map. The left side is about pragmatic considerations and application. The right side is about belief and anticipation. Where are your views within this landscape?
Adjust level here
Now move the slider on the lower right to select the 15-cluster view. Hover over clusters like "Deepseek breakthrough", "Anthropic claims" or "Sam Altman credibility". These are on the right side of the map because each of them pertains to anticipation and belief. Sam Altman is an interesting example, to the extent that as a CEO he tends to espouse long term visions, more than technical details. It makes perfect sense that his brand - as defined by the hivemind of conversations online - is in the belief section of the map, rather than the the pragmatic section.
Over time - what's changing?
The below time series view shows how each narrative has shifted in the past 18 months.
Trending up: It's personal! Three clusters near the bottom of the map are trending significantly up. Both Advancement vs Status quo, and Change: reflections on value reflect that the GPT conversation is growing more contentious. Each of these cluster reflect tensions - or a strong personal view on the use of this technology. Exploration: personal and daily use is another trending narrative - a conversation about daily, mundane and entertaining uses of GPT's
Trending down: Industry and productivity narratives: Conversely, many of the industry-focused narratives at the top of the map are dropping over time, as is the productivity-focused cluster near the left side. What do you make of this?
Narrative breakdown, by country
The below bar chart shows each of the 15 clusters, split by country. For example, "Sam Altman credibility" is largely comprised of US responses.
Hover over the bars in the chart to see breakdowns by country - or click on squares on the legend on the right to see which countries are more vs less represented in each narrative.
What is unique about narrative analytics, compared to other approaches?

~10
2568
1. Every map is unique: Nothing is pre-set
Each map is unique to the dataset, and unique to your data. Narrative maps are created from a huge number of possible combinations of clusters - based on the unique views expressed within your data. This means the analysis is tailored to your business. For this reason, the clusters in narrative maps often correlate more strongly to outcomes, compared to standard one-size-fits all approaches or performance models.
possible cluster/axis combinations
Most data dashboards rely on structured data which measures behaviour and outcomes: these are lagging indicators which can leave teams reacting to the scores. Narratives often change before the inflection point when outcomes are decided. For this reason, narrative analytics can help companies intercept early signals in their business, to more proactively manage their business.
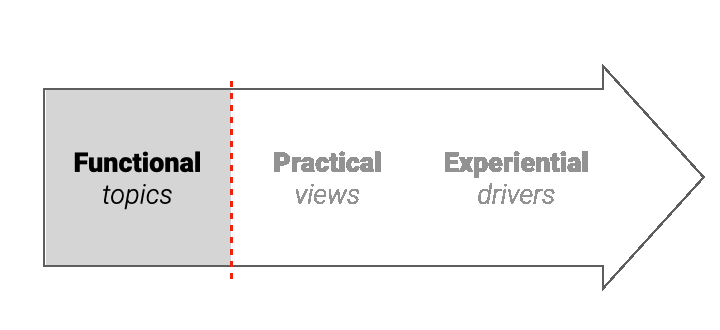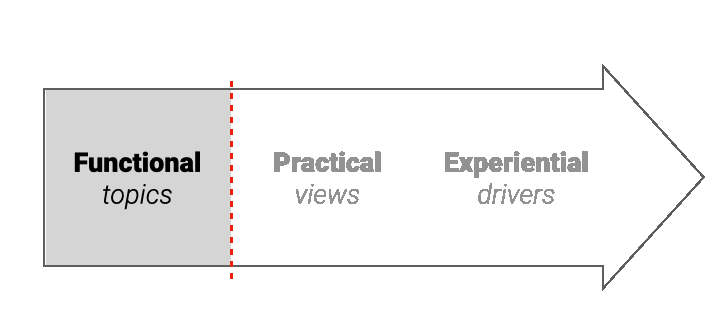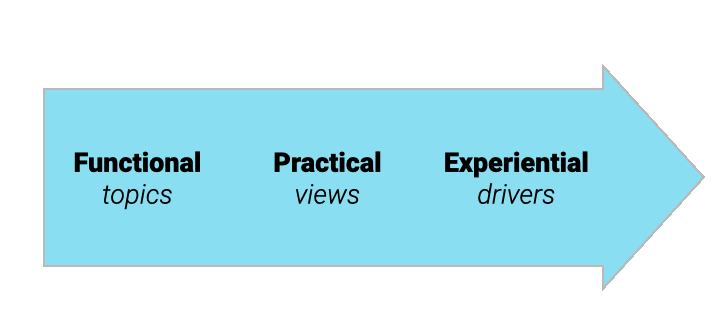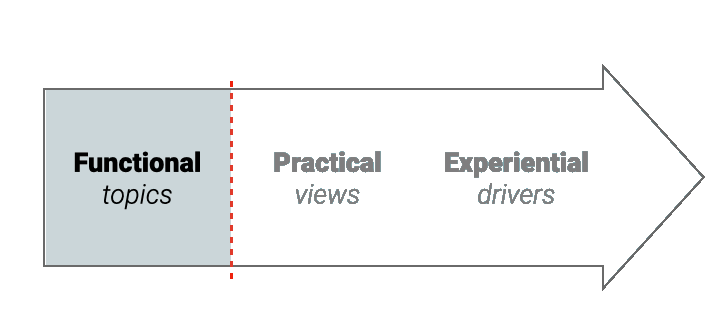
2. Narratives - not just topics
Standard analytical techniques capture topics. A narrative is bigger than a topic, capturing real-world context and experiential drivers:
This allows teams to understand the "reason why" behind the scores. The result is faster, clearer understanding and actionability.

VS

AI Chatbots:
built to talk
Phrasia
built to hear
3. How does it compare to AI chatbots?
Narrative analytics is built on some of the same LLM and deep learning technology as AI chatbots. However, with narrative analytics, the algorithm is 100% focused on hearing, not talking.
Chatbots are designed to give the 'most likely' response to a question. By design, they provide the 'conventional' answer, ignoring outliers which may signal emerging risks and opportunities. Narrative analytics reveals the full landscape, making it easy to detect outliers, and emerging themes, as well as the most common issues.
4. Supporting - not replacing - human judgement
Narrative analytics is designed to involve and engage
people. The transparency of the narrative maps make it easy
to involve non-technical stakeholders in refining and improving
the maps.

VS
Leading
indicators
5. Leading indicators for faster action
Lagging
indicators

Narrative analytics: An introduction for MUFG
In collaboration with The Human Factor, this shares several interactive narrative maps to demonstrate the potential of Narrative Analytics capability. By exploring and interacting with the narrative maps, teams can discover and measure the drivers in their business, through the voice of their employees and customers. Although the deep learning technology used for narrative analytics is complex, we have designed the approach to be intuitive for non-technical people. Before you get started, below are some simple tips.

1. Every dot is a statement
Each dot in a map represents a unique, full statement made by a person, with each of the dots arranged into clusters. Hover over the dots with your cursor to read some of the statements. Each statement appears only one time in a narrative map
2. Look at the levels
Each map has high level themes which show the axes. Note that the axes are opposites, from left to right and top to bottom. Use the slider to see the more detailed narratives within the high level themes. This helps you see the full shape of the conversation.


3. Consider the surrounding clusters
Clusters appear near other clusters which are similar in meaning. By looking at the clusters within the "neighbourhood" of clusters near by, you can understand the related issues experienced by employees.
4. Zoom in
On PC, use Ctrl +/- to make the dots and text bigger or smaller (Command +/- on Mac). To explore a specific cluster or part of the map more carefully, you can use the zoom function at the top right. Select it, then you can click and drag to select the area you want to explore. When you click the "home" icon, the map will return to normal.


5. Consider the 98%
The map provides a '98% view' of the landscape. In classifying thousands of statements into just 20 or 30 narrative clusters, there are always some that don't fit perfectly. Still, a 98% view is a significant step forward compared to subjective opinions, or other technologies which only capture perhaps 50% of the drivers.
6. Focusing on the signal, versus the noise
By modelling narratives against other data such as eNPS, review scores, etc, companies can make better decisions on what to focus on, and more quickly create an action plan based on a better understanding of drivers. This also helps teams decide what NOT to do. Narrative analytics can also be a strong foundation for predictive analysis, applied to customer or employee churn, sales growth, commodities prices, and more.

